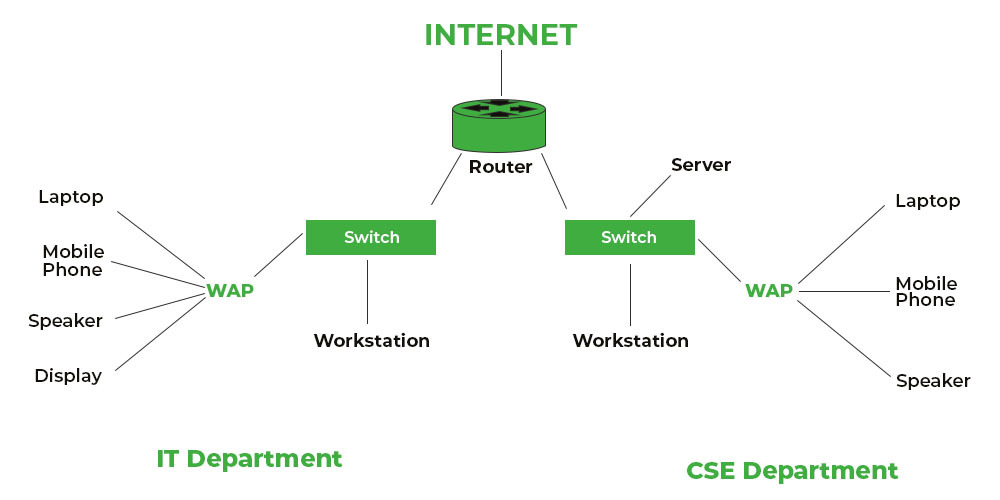
Network switches are available in various types and categories to address different use cases. These are:
1. Managed switches
Managed switches, most commonly seen in commercial and enterprise settings, provide greater capacity and capabilities for IT experts. To configure managed switches, command-line interfaces are utilized. They enable simple network management protocol agents, which offer information for troubleshooting network issues.
Administrators can also use them to create virtual LANs to split a local network into smaller parts. Managed switches are substantially more expensive than unmanaged switches due to their additional functionality.
2. Unmanaged switches
The most basic switches are unmanaged switches, which have a set configuration. An unmanaged switch merely expands a LAN’s Ethernet connections, allowing additional internet connections to local devices. Unmanaged switches use device
MAC addresses to transmit data back and forth. They are usually plug-and-play, meaning the user has few alternatives to pick from.
These switches could have default configurations for aspects like quality of service, but one cannot modify them. Unmanaged switches are relatively cheap, but poor capability renders them unsuitable for many corporate applications.
3. Power over ethernet (POE) switches
PoE capabilities are now available on some
network switches, making installing IoT devices and other gear faster, simpler, and safer. PoE is a method of supplying DC power to low-power devices across a LAN wire. Low-power devices connected to a PoE-capable network switch will no longer require a power supply. When concealing connections isn’t possible, this avoids the need for additional power outlets and makes the installation seem efficient. A PoE-capable switch is also safer because the power output is low and intelligently managed.
4. Local area network (LAN) switches
LAN switches, or local area network switches, are typically used to link locations on a company’s internal LAN. It also is referred to as an Ethernet switch or a data switch. Allocating bandwidth efficiently prevents data packets from overlapping as they travel via a network. Before directing the delivered data packet to its intended destination, the
LAN switch delivers it. These switches alleviate network congestion or bottlenecks by sending a packet of data solely to its intended receiver.
5. Smart switches
Managed switches are called smart or intelligent switches when they have characteristics that go beyond an unmanaged switch but are less than a conventional managed switch. They are therefore more advanced than unmanaged switches but less expensive than fully controllable ones.
Other alternatives, such as
VLANs, may not offer as many functions as fully controlled switches. However, because they are less costly, they may be suitable for smaller networks with limited budgets and fewer feature requirements.
6. Modular switches
Modular switches allow you to add extension modules as needed, providing greater flexibility as the network grows. Expansion modules for wireless connection, firewalls, and network analysis are some examples of app-specific expansion options.
Additional connections, power sources, and cooling fans may be possible. However, these switches are significantly more expensive than fixed ones and often employed in massive networks. In most cases, they also include Layer 3 capabilities (in addition to Layer 2), allowing them to operate as network routers.
7. Fixed-configuration switches
Fixed-configuration switches feature a fixed number of ports and are often not expandable, making them affordable over time. The most common switches on the market are these. They have a predetermined number of
Ethernet ports, for example, 8 Gigabit Ports, 16 ports, 24 ports, and 48 ports, among others. They can have a variety of ports (in terms of speed and connection). However, port speeds are typically 1 Gbps (at the very least), and connectivity choices are either wired electrical ports (RJ45) or optical fiber ports.
8. Stackable switches
Stackable switches allow you to optimize your network while also increasing its reliability. With an actual stackable switch, these clusters of switches function as a single switch powered by a single SNMP/RMON agent, one domain, just one command line interface (CLI), or a Web interface.
The ability to create link aggregation groupings covering several units in the stack, transfer mirror traffic from one component to another in the stack, and configure
Quality of Service (QoS) encompassing all units are all advantages of using these types of switches for connection.
9. Layer three switches
Switches are part of the OSI model’s Layer 2 layer. They function at the data network layer, and their main job is to forward ethernet frames as quickly as possible from one port to another. Because they operate at the Network Layer of the OSI model, these switches are referred to as Layer 3 switches. A Layer 3 switch is a hybrid of Layer 2 and 3 devices. Their software is more complex than traditional Layer 2 switches, and they can run dynamic routing protocols.
10. Data center switches
Data centers have exploded in popularity in recent years. Almost all major organizations consolidate their IT assets and networks into a few large data centers for easier administration, management, and other reasons. As a result, data center switches must-have features like high-speed performance, huge port capacity, low latency, virtualization support, security, and QoS, among others.
The Cisco Nexus range of devices is an excellent example of
Data Center switches. These switches are ideal for implementing the
software-defined network (SDN) concept and providing virtualization and programmability.
11. Switches with optical fiber ports
The RJ45 connector connects to a standard ethernet cable and is the most common switch interface. In many circumstances, you’ll need to employ a fiber-optic connection to extend connectivity beyond the 100-meter limit of standard ethernet cables. Switches with optical fiber ports often have RJ45 ports and additional
fiber optic ports for connecting to fiber connections.
Small-form factor pluggable fiber optic ports are what they’re called. In most cases, optical fiber ports are utilized to connect to other remote switches, either inside the same building or across facilities located kilometers apart.
12. Keyboard, video, and mouse (KVM) switch
This switch connects
numerous computers to a keyboard, mouse, or monitor. These switches are frequently used to control groups of servers while removing cords from the desktop. A KVM switch is an excellent interface for a user who wants to handle many machines from a single console. Keyboard hotkeys may typically be configured into these devices, allowing you to switch between PCs quickly. A KVM extender may bolster the switch’s reach by several hundred feet to transmit DVI, VGA, or HDMI video transmissions.
See more information: – network.sciencefather.com
Nomination : Nominate Now
Contact us : network@sciencefather.com
Social Media :
#sciencefather #researcher #researchscientist #speaker #networkingevents #tech #internet #technology #system #software #networkcoding #globalnetwork #wifi #5g #5Gspeed #cybersecurity #cloudcomputing #datascience #iot #ai #blockchain #bigdata #techinnovation #webdevelopment #wireless #technews #computerscience #dataanalytics