Website link: https://networking-
Friday, March 31, 2023
4th Edition of International Research Awards on Network Protocols, on 27...
Website link: https://networking-
#bluetooth #topology #webs #fiberoptics #lan
#protocols #bandwidth #servers #firewall
Saturday, March 25, 2023
Star Topology | protocols | internet | server | webs |
Twitter: https://twitter.com/
#bluetooth #topology #webs #fiberoptics #lan
#protocols #bandwidth #servers #firewall
Tuesday, March 21, 2023
Layers of OSI model | network | protocols | topology | servers |
Website link: https://networking-
#fiberoptics #lan #servers #firewall #webs
#bluetooth #topology #protocols #bandwidth
Network theory | webs | protocols | LAN | bandwidth |
Website link: https://networking-
#bluetooth #topology #webs #fiberoptics #lan
#protocols #bandwidth #servers #firewall
Monday, March 20, 2023
Sunday, March 12, 2023
Types of Internet Services

To exchange data/information among individuals or organizations, the internet enables communication services. This mainly includes VoIP and video conferencing.
Voice over internet protocol (VoIP) enables users to place voice calls over the internet compared to a conventional (or analog) phone connection. Other VoIP services allow you to contact anybody with a mobile number, encompassing long-distance, cellular, and even local/international connections.
Video conferencing technology enables two or more individuals in separate locations to connect visually and in real time. It includes persons in different places using video-enabled devices and broadcasting real-time speech, video, texts, and slideshows via the internet.
We utilize file transfer to exchange, transmit, or send a document or logical data item among many individuals or computers, both locally and remotely. Data files may comprise documents, videos, photos, text, or PDFs. They may be shared via internet downloading and uploading. File transfer protocol (FTP) is one of the most common internet protocols used for this purpose.
3. Directory services
A directory service is a collection of software that maintains information about the organization, its customers, or both. Directory services are responsible for mapping network resource names to network addresses. It offers administrators and users transparent access to all network computers, printers, servers, and other devices. It is also an important backend service provider for and by the internet.
Domain number system (DNS) and lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) are the most commonly used directory services. A DNS server stores a map of computer hostnames and other domain names to IP addresses. LDAP is a collection of open protocols to obtain centralized network access to stored data. It is also a mechanism for cross-platform authentication.
Ecommerce allows the customer to purchase a service or product directly from the vendor, at any time or anywhere on the planet. When IBM started offering hardware and software for computers over the internet, it was one of the first instances of ecommerce. Since then, this service has grown in use tremendously. Ecommerce uses the web to enable financial exchanges so that data packets can translate into their real-world monetary equivalents.
Network management services are some of the most critical and valuable internet services for IT administrators. They assist in avoiding, monitoring, diagnosing, and resolving network-related issues. Two services are mainly used for this purpose – ping and traceroute.
The ping utility checks the host machine’s availability and the time required to react to any and all internet control message protocol (ICMP) transmissions. It guarantees that all requests issued by a computer reach the web server without packet loss. In the meantime, the traceroute identifies and displays all potential paths from query to response, as well as the turnaround time for each route.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) or Coordinated Universal Time synchronizes computer clocks (UTC). Network time protocol (NTP) is an established internet time service that syncs and adjusts the computer clock accurately to all these standards. All Windows time variants released after Windows 2000 synchronize with an NTP server. NTP sec is primarily a secured version of NTP.
When users search for a web page through a search engine rather than the domain name, the search engine examines the web crawler’s index of all pages. It will study the search phrase and compare it to the database, including how often the search terms appear on a webpage, where they appear on the site, whether they appear together, etc. It analyzes this information to determine which websites best fit your search query.
Website link: https://networking-
Twitter: https://twitter.com/
#topology #webs #fiberoptics #bandwidth
#network #protocols #servers #bluetooth
Meaning of Internet...
The internet is a global network of devices that communicate using the TCP protocol.
The internet is defined as a global network of linked computers, servers, phones, and smart appliances that communicate with each other using the transmission control protocol (TCP) standard to enable the fast exchange of information and files, along with other types of services.
This article explains the meaning, inner workings, and the most popular types of internet.
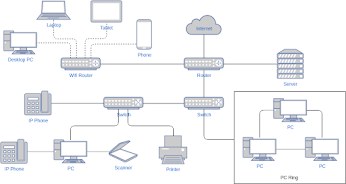
The internet is a global hub of computer networks — a network of connections wherein users at any workstation may, with authorization, receive data from every other system (and often interact with users working on other computers).
Internet infrastructure comprises optical fiber data transmission cables or copper wires, as well as numerous additional networking infrastructures, such as Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), etc. Sometimes wireless services such as 4G and 5G or WiFi necessitate similar physical cable installations for internet access.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) in the United States controls the internet and its associated technologies, such as IP addresses.

The internet was first envisioned in the form of ARPANET by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. government in 1969. The initial goal was to create a network that would enable users of a research computer at one institution to “communicate” with research computers at another institution. Since communications can be sent or diverted across several directions, ARPANet could continue to operate even if a military strike or any other calamity damages portions of the network.
ARPANET used the new packet switching technology to create low-cost, interactive interactions between computers, which generally communicate in short data bursts. Packet switching broke down large transmissions (or portions of computer data) into smaller, more manageable parts (called packets) that could travel independently across any accessible circuit to the destination where they were reassembled.
Countless people utilize it as their primary source of data consumption, spurring the development and expansion of their own community through social networking and content exchange. However, private versions of the internet do exist, which are primarily used by large organizations for secure and regulated information exchange.
Key features of the internet
The internet is a vast, interconnected network of computers and other network-enabled devices, which is:
Globally available:
The internet is an international service with universal access. People living in isolated areas of an archipelago or even in the depths of Africa can now access the internet.
Easy to use:
The software used to connect to the internet (web browser) is user-friendly and easy to understand. It’s also relatively easy to create.
Compatible with other types of media:
The internet provides a high level of engagement with photos and videos, among other media.
Affordable:
Internet service development, as well as maintenance costs, are modest.
Flexible:
Internet-based communication is highly adaptable. It supports text, audio, and video communication. These services are available at both individual and organizational levels.
Website link: https://networking-
#protocols #servers #bluetooth #network
#bandwidth #topology #webs #fiberoptics
How Does the Internet Work

The internet delivers different types of information and media across networked devices. It operates using an Internet Protocol (IP) and a Transport Control Protocol (TCP) packet routing network. Whenever you visit a website, your computer or mobile device requests the server using such protocols.
The server accesses the web page and delivers the right information to your computer whenever the request arrives. This is broadly the end-to-end user experience. Let us now look at the more technical details of how the internet works.
The basic foundation of the internet is an interconnected network of computers. When two computers interact, they must be physically (often via an Ethernet connection) or wirelessly connected (via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth). All modern systems can support any of these connections to establish a core network.
The Computer Network, as described above, is not restricted to two PCs. One can link several computers. However, as you expand, it may get more complex. Every machine on a network is connected to a tiny computing device known as a router to address this problem. This router’s only function is to operate as a signaler. It ensures that a message transmitted from a particular computer reaches its intended recipient. With the addition of a router, a system of 10 computers needs merely ten wires instead of 10 × 10 = 100 connections.
Let us now discuss interconnecting hundreds of thousands to billions of machines. A single router cannot scale to that extent; nonetheless, a router is an independently programmable computer unit. This implies that two or more routers may be connected, enabling infinite scaling.
By now, we have constructed a network identical to the internet, although it is only intended for individual use and cannot connect with the outside world. This is where public infrastructure comes in. The telephone system links an office to everyone worldwide, making it the ideal wiring configuration for the internet. A modem is necessary for connecting networks to the telephone system. This modem converts data from a network into data that can be managed by the telephony architecture and vice versa.
The following step is to transmit the information from your network to the target network. To accomplish this, the network must establish a connection with an internet service provider (ISP). An ISP is a service that administers specified routers that are interconnected and also have access to the routers of other ISPs. Therefore, the data from the host network is delivered to the target network via the web of ISP networks.
6. Assigning domain name to IP addresses
IP addresses are intended for computers, but in an infinitely extensible internet, it would be difficult for people to keep count of an ever-growing number of addresses. To simplify matters, one may designate an IP address with a domain name, a human-readable name. Google.com is an excellent example of this — the domain name is used in conjunction with the IP address 142.250.190.78. Therefore, typing the domain name is the simplest way to access a computer online.
The internet is a network architecture that enables millions of machines to communicate with one another. Several of these machines (web servers) can feed web browsers intelligible messages. The web is an application constructed on top of the internet’s infrastructure. It is important to note that additional services, like email, have been developed on top of the internet.
Intranets are personal and bespoke networks confined to an organization’s members. They offer participants a secure gateway to access shared information, collaborate, and communicate.
Extranets are quite similar to intranets, except that they enable collaboration and sharing with other businesses. Typically, they are employed to safely and confidentially transmit information to customers and other enterprise stakeholders. Frequently, their functions resemble those of an intranet: file and information sharing, collaboration tools, message boards, etc. Intranets and extranets operate on the same infrastructure and adhere to the same protocols as the internet.
How does the web work?
When we discuss the internet in common parlance, we typically refer to the web – although the two terms are not interchangeable. If the internet can be understood as a network of highways, then the web will be the network of restaurants, toll booths, gas stations, etc., built along it.
On the other hand, the web comprises multiple computers connected to the internet called clients and servers.
Clients are internet-connected devices of a web user (such as a computer linked to Wi-Fi or a mobile phone) and the online-accessing software installed on such systems (generally a web browser).
Servers store websites, applications, and their associated data and activities. When a client device requests access to a website, a replica of the webpage is received from the server to the client’s computer. The webpage is then exhibited in the client’s web browser.
The browser then transmits an HTTP or HTTPS request message back to the server, asking the server to transmit a copy of the web page to the client. This message and all other data transferred between the client and server are sent via the TCP/IP protocol across your internet connection.
Website link: https://networking-
#webs #fiberoptics #network #protocols
#bandwidth #servers #bluetooth #topology
Friday, March 10, 2023
Microsoft Internet Explorer bids final goodbye to its users after 28 years of service
Microsoft's Internet Explorer, which debuted in 1995 as an add-on package with Windows 95, has been decommissioned following the release of a Microsoft Edge update on specific Windows 10 devices yesterday. The platform, which had no security support, is now dead and inaccessible.
Back in 2003, Internet Explorer was one of the most popular web browsers, with over 95% market share, but it suffered a decline after Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome entered the market. Notably, Mozilla Firefox debuted in 2004 and Google Chrome debuted in 2008.
The company clearly stated on its frequently asked questions page that the Microsoft Edge update was pushed to all users and devices, both commercial and consumer.
Users won't be able to undo the Microsoft Edge update, which will be pushed simultaneously to all business and consumer devices. Furthermore, Internet Explorer 11 redirection to Microsoft Edge will be included in all future Microsoft Edge releases "Microsoft's FAQ website was written.
For Windows 10 users, Microsoft Edge will automatically transmit browsing information, including bookmarks. If you click any Internet Explorer icon or try to launch it from the Start or Run menus, Edge will ..
Meanwhile, Microsoft has launched Bing, a Chat GPT-powered search engine, with the goal of Revolutionising overall searches and answering all advanced queries. Furthermore, the company has announced a multi-billion dollar agreement with Open AI, the Chat GPT-developer.
Website link: https://networking-
#bluetooth #topology #webs
Tuesday, March 7, 2023
The internet did it: the downfall of the news and the dismay of the young
First, the news. There’s not a lot left. We’re misled in Toronto because we still have four functioning newspapers but everywhere, newsrooms are pared or closed, journalists fired or bought out, stories go untold. This is wretched for democratic health. Other things, like shattered careers or profits, matter less.
It happened because ads, the main source of news media income, migrated massively to internet giants like Google and Facebook. So the government has introduced a bill (C-18) modelled on an Australian law, requiring big platforms that conscript stories from news outlets to “compensate journalists when they use their work.”
News media did an often wretched, but also often enough useful, job of filling that need, and to do it you need big resources, not piddly ones. No number of earnest, honest journalists with independent voices on Substack can properly dig into urgent subjects like Doug Ford and the Developers. They can comment on those but can’t generate them.
The point is the ads are mostly gone and the institutions are mostly (like Westley in “The Princess Bride”) dead. A government that cares can either fund news directly, like the CBC, or impose taxes and transfer the funds, or force the Googles to share with the news outlets, as the current bill does.
She said it can be statistically best correlated not with real world bummers like climate and war but with “the deleterious psychological effects of social media.”
This week, too, right wing U.S. senator Josh Hawley, tabled a bill banning kids under 16 from using social media. Ontario’s People for Education reports a worrying rise here in poor mental health among the young, though not linking it to social media.
Humanity’s existential baseline in the past was mostly to be alone, though sometimes not. You could be out with your flock in the field, or walking to the 7-Eleven at night for groceries. Nobody knew exactly where you were. If you saw someone yapping on the street, they were probably deranged. Now they’re just on their phone.
Now don’t forget how miserably alone adolescence can be. In that light, internet connectedness is a hope-filled potential resource — provided, to be sure, it isn’t a substitute for actual in-person interaction with those you care about. Maybe the role of the old(er) should be to remind the young, when it’s needed, of how important a balance can be, versus tossing them offline altogether.
Website link: https://networking-
#ethernet #gigabit #fiberoptics #firewall
#protocols #bandwidth #servers
Saturday, March 4, 2023
Network Security Platform | WAN | Internet | WWW | LAN |
Twitter: https://twitter.com/
#bandwidth #fiberoptics #protocols
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
The evolution of wireless communication networks has been a remarkable journey, shaping how we connect and communicate. Here’s a concise ove...
-
In today's increasingly digital world, the need for secure online communication is more crucial than ever. Whether it's personal i...
-
When discussing Types of Technology , we can categorize them based on their applications, functionalities, and impact on society. Below is...




