The internet is a global network of devices that communicate using the TCP protocol.
The internet is defined as a global network of linked computers, servers, phones, and smart appliances that communicate with each other using the transmission control protocol (TCP) standard to enable the fast exchange of information and files, along with other types of services.
This article explains the meaning, inner workings, and the most popular types of internet.
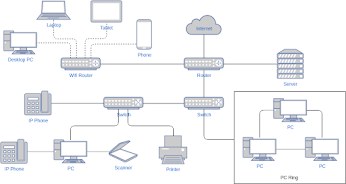
The internet is a global hub of computer networks — a network of connections wherein users at any workstation may, with authorization, receive data from every other system (and often interact with users working on other computers).
Internet infrastructure comprises optical fiber data transmission cables or copper wires, as well as numerous additional networking infrastructures, such as Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), etc. Sometimes wireless services such as 4G and 5G or WiFi necessitate similar physical cable installations for internet access.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) in the United States controls the internet and its associated technologies, such as IP addresses.

The internet was first envisioned in the form of ARPANET by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. government in 1969. The initial goal was to create a network that would enable users of a research computer at one institution to “communicate” with research computers at another institution. Since communications can be sent or diverted across several directions, ARPANet could continue to operate even if a military strike or any other calamity damages portions of the network.
ARPANET used the new packet switching technology to create low-cost, interactive interactions between computers, which generally communicate in short data bursts. Packet switching broke down large transmissions (or portions of computer data) into smaller, more manageable parts (called packets) that could travel independently across any accessible circuit to the destination where they were reassembled.
Countless people utilize it as their primary source of data consumption, spurring the development and expansion of their own community through social networking and content exchange. However, private versions of the internet do exist, which are primarily used by large organizations for secure and regulated information exchange.
Key features of the internet
The internet is a vast, interconnected network of computers and other network-enabled devices, which is:
Globally available:
The internet is an international service with universal access. People living in isolated areas of an archipelago or even in the depths of Africa can now access the internet.
Easy to use:
The software used to connect to the internet (web browser) is user-friendly and easy to understand. It’s also relatively easy to create.
Compatible with other types of media:
The internet provides a high level of engagement with photos and videos, among other media.
Affordable:
Internet service development, as well as maintenance costs, are modest.
Flexible:
Internet-based communication is highly adaptable. It supports text, audio, and video communication. These services are available at both individual and organizational levels.
Website link: https://networking-
#protocols #servers #bluetooth #network
#bandwidth #topology #webs #fiberoptics



No comments:
Post a Comment