Computer Network Components
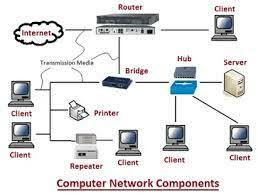
Computer networks components comprise both physical parts as well as the software required for installing computer networks, both at organizations and at home. The hardware components are the server, client, peer, transmission medium, and connecting devices.
Types of computer networks:
Depending on the organization's size and requirements, there are three common types of enterprise private networks:
1.Local area network (LAN): It is a group of computers and peripheral devices that share a common communications line or wireless link to a server within a distinct geographic area.
2.Wide area networks (WAN): It is a geographically distributed private telecommunications network that interconnects multiple local area networks (LANs)
3.Prsonal area network (PAN): A PAN is most commonly used for one individual and to connect just a handful of devices such as a computer, smart phone, and printer.
4.Metropolitan area network (MAN): Larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, a MAN incorporates elements of both types of networks. Ownership and management can be handled by a single person, but it’s more likely done by a larger company or organization.
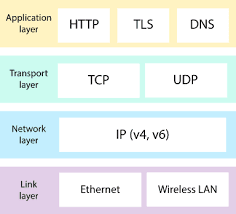
A network protocol is an established set of rules that determine how data is transmitted between different devices in the same network. Network protocols are the reason you can easily communicate with people all over the world, and thus play a critical role in modern digital communications.
Types of network protocol:
1.Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol a communications standard that enables application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network.
2.Internet Protocol (IP): Internet Protocol (IP) is the method or protocol by which data is sent from one computer to another on the internet.
3.User Datagram Protocol (UDP): What is UDP protocol used for?
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) refers to a protocol used for communication throughout the internet.
4.Post office Protocol (POP): POP3 is designed for receiving incoming E-mails.
5.Simple mail transport Protocol (SMTP): SMTP is designed to send and distribute outgoing E-Mail.
6.File Transfer Protocol (FTP): FTP allows users to transfer files from one machine to another.
7.Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP): Through the HTTP protocol, resources are exchanged between client devices and servers over the internet.
8.Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS): Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a protocol that secures communication and data transfer between a user's web browser and a website.
Website : sciencefather.com
See more Info : - network.sciencefather.com
Nomination : https://x-i.me/prinom
Registration : https://x-i.me/prireg2
Contact us : network@sciencefather.com
Social Media :
Instagram : https://x-i.me/net23m
Pinterest : https://x-i.me/net23p
Facebook : https://x-i.me/net23f
Youtube : https://x-i.me/NQGu
#sciencefather #researcher #scifax #research #technology #Networking #Ethernet #Networking #Cabling #Cat5e #Cat6 #TwistedPair #DataTransmission #WiredConnection #NetworkInfrastructure #InternetAccess #networkanalysis #networkmarketing #protocols #network #5g #cybersecurity #cloudcomputing #blockchain #TechTrailblazers




No comments:
Post a Comment